Many projects that our team of scientists have been involved in for the last 10 years or more were precursors to the BioSAFE project. They were projects that highlighted the need to further investigate invasive alien species to Canada. Genome Canada, British Columbia and Quebec are funding agencies of genomic research in Canada that have provided funding for much of this work. Other collaborators have also included the Canadian Food Inspection Agency and Natural Resources Canada. Though the funding is complete for these projects, there is still output of publications, protocols and outreach workshops that we would like to share with the public. Below are some of the latest news and background information for these previous projects.
Genomics Application Partnership Program (GAPP)
Latest news
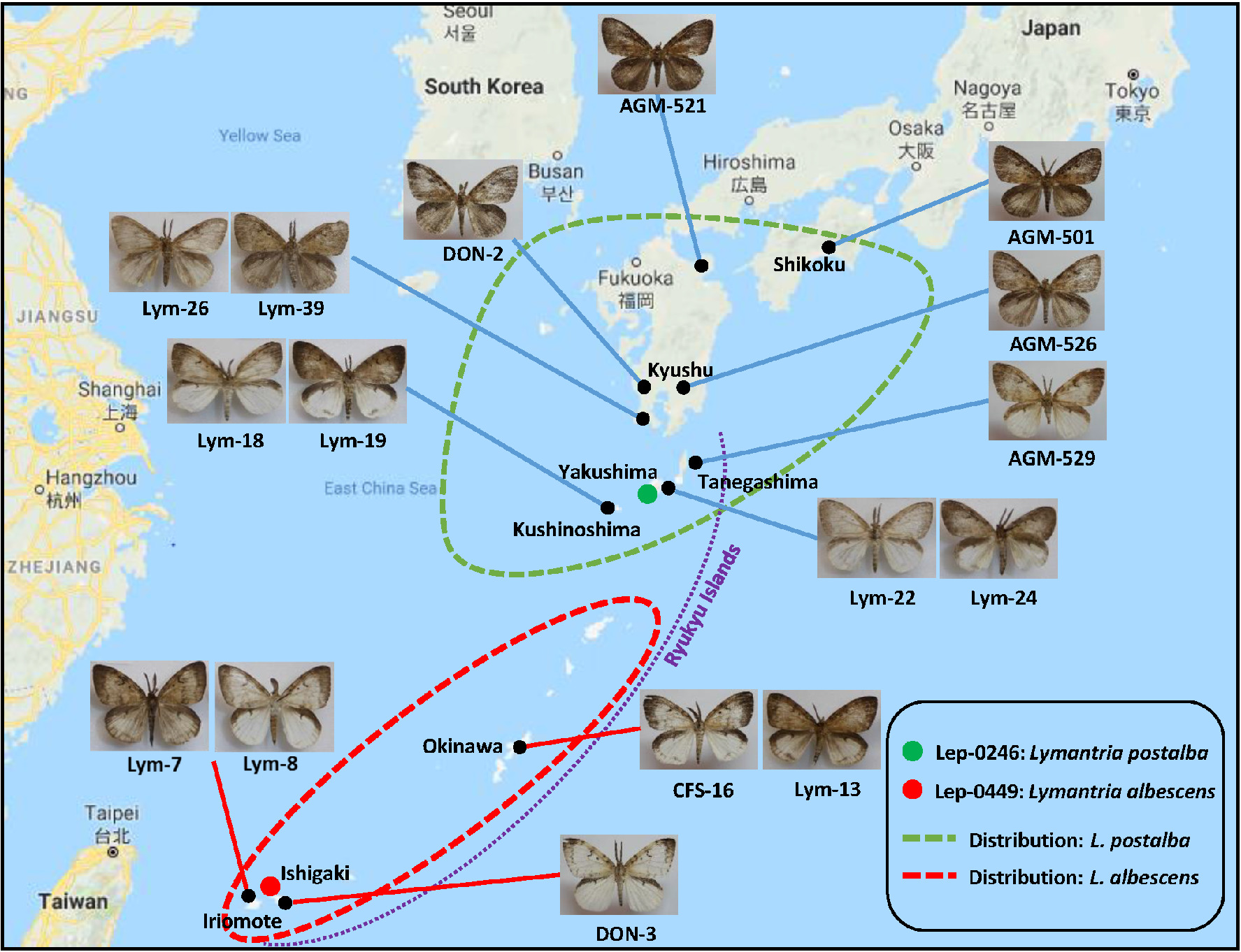
Reassessment of the status of Lymantria albescens and L. postalba (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Lymantriinae) as distinct “Asian gypsy moth” species, using both mitochondrial and nuclear sequence data.
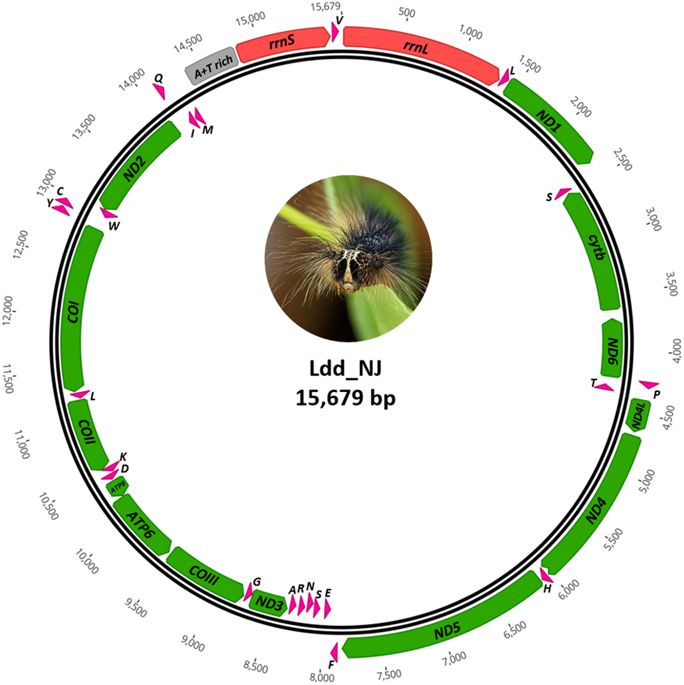
Limiting risk of AGM gypsy moth invasion by looking at the mitochondrial barcode region of 10 geographic variants of L. dispar
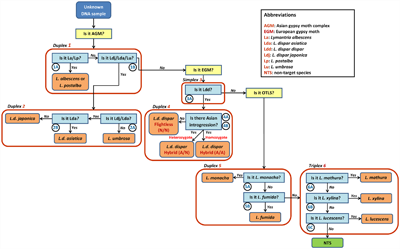
Assays for the rapid and accurate identification of ten Lymantria species and subspecies to protect forest resources from forest invasive alien species
Background, Methods and Outcomes
Background
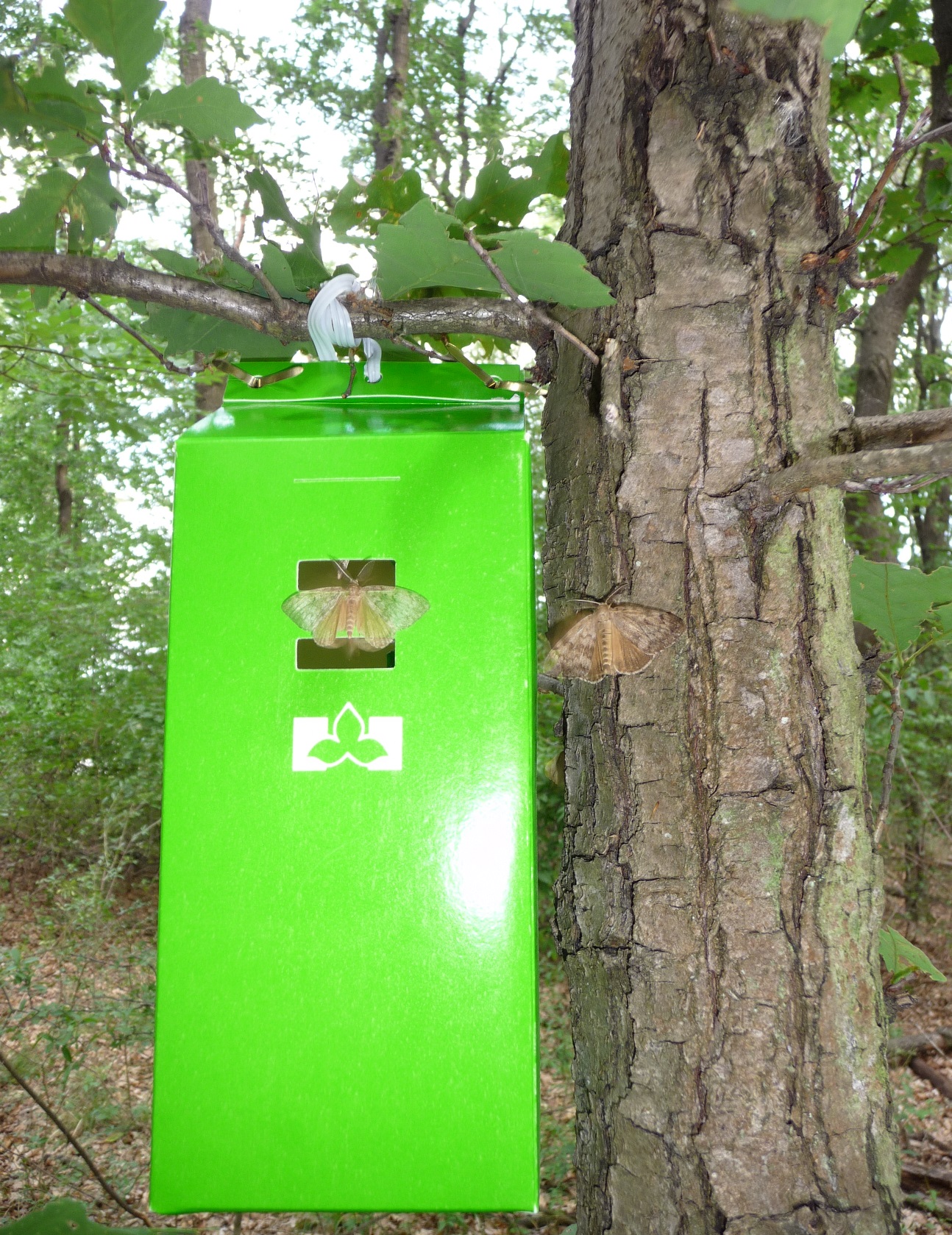
To prevent Forest Invasive Alien Species (FIAS) from establishing in Canada and causing an outbreak, our border agencies and regulatory inspectors need to be equipped with tools to rapidly and accurately identify such FIASs. In the Genome Canada, BC and Quebec funded Genomics Application Partnership Program (GAPP) project from 2012-2016, the team targeted the Asian gypsy moth (AGM) and the sudden oak death (caused by Phytophthora ramorum, PR). These pest and pathogen were identified by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) as among the most important threats to Canada’s forests and trees. As deliverables from this project, suites of diagnostic tools were developed that provide accurate, efficient and cost-effective detection of these IAS. The tools can be used with all life stages of the organisms (eggs, larvae, adults, infected plant tissues) and received rigorous validation, including national multi-laboratory blind tests that confirmed their reliability and efficiency. [Picture courtesy of Christa Schafellner]

Methods
Asian gypsy moth and sudden oak death (caused by Phytophthora ramorum) pose significant threats to the Canadian forest and related industries. Our team used a bioinformatics pipeline and genomic resources from our current and previous Large Scale Applied Project, TAIGA project (@TAIGALab) to develop DNA detection arrays that targeted genomic regions of AGM and PR with greater accuracy and speed than previously possible.
Outcomes
We developed three tiers of PR multiplex qPCR assays that can determine the lineage (NA1, NA2, EU1 and EU2), species (P. ramorum) and genus (Phytophthora) of a sample.
A molecular identification key was designed by developing a suite of AGM qPCR TaqMan assays that allow the identification of AGM, the European gypsy moth (EGM) and other potentially damaging Lymantria species, from individual samples. A separate TaqMan assay was also developed for the detection of rare AGM speciemens in bulk pheromone trap samples, which typically contain only EGM in North America.
Publications
Stewart D, Nisole A, Djoumad A, Zahiri R, Lamarche J, Levesque RC, Hamelin RC, Cusson M
(2019) A needle in a haystack: a multigene TaqMan assay for the detection of Asian gypsy moths in bulk pheromone trap samples. Biol Invasions https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-019-01943-9
Djoumad A, Nisole A, Zahiri R, Freschi L, Picq S, Gundersen-Rindal DE, Sparks ME, Dewar K, Stewart D, Maaroufi H, Levesque RC, Hamelin RC, Cusson M
(2017) Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes of geographic variants of the gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar, reveals a previously undescribed genotypic entity. Sci Rep 7, 14245
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-14530-6
Stewart D, Zahiri R, Djoumad A, Freschi L, Lamarche J, Holden D, Cervantes S, Ojeda DI, Potvin A, Nisole A, Béliveau C, Capron A, Kimoto T, Day B, Yueh H, Duff C, Levesque RC, Hamelin RC, Cusson M.
(2016) A multi-species TaqMan PCR assay for the identification of Asian gypsy moths (Lymantria spp.) and other invasive lymantriines of biosecurity concern to North America. PLoS ONE 11, e0160878.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160878

